CEF(CVV)/DA series 0.6/1KV EPR(PVC、NR+SBR) Insulated power cables for ships and Marine construction
Product Description
Marine power cable is a kind of marine cable, which is used for power, lighting and general control of various ships and offshore oil platforms in rivers and seas. Marine power cable plays an important role in the marine power system and is the lifeblood of the whole ship. It is responsible for the transmission and distribution of electric energy for various electrical equipment on board.
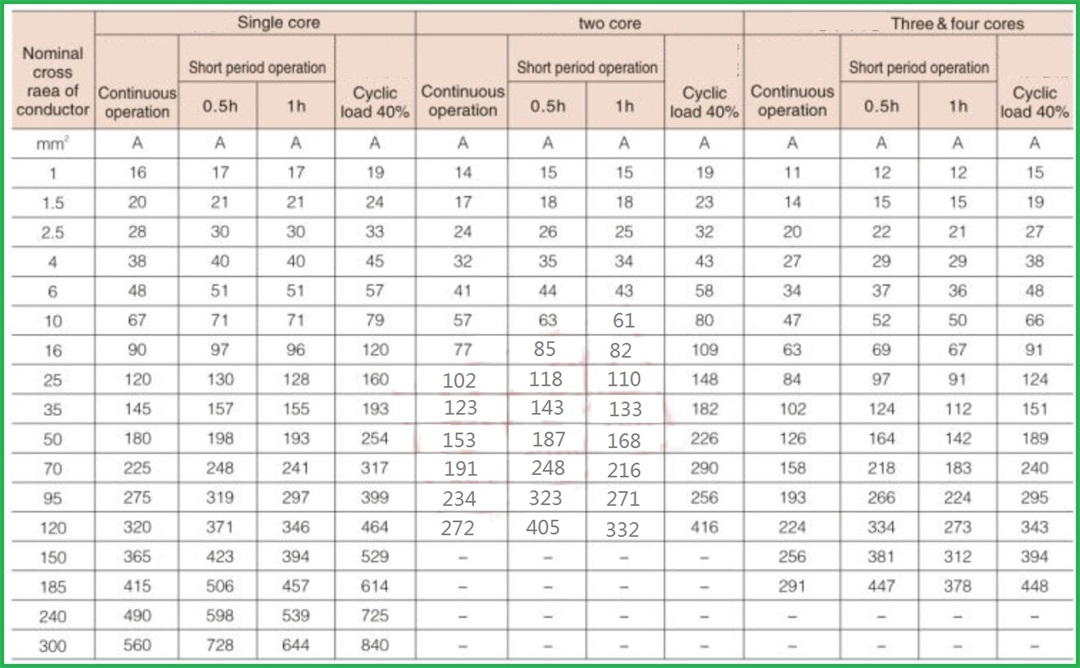
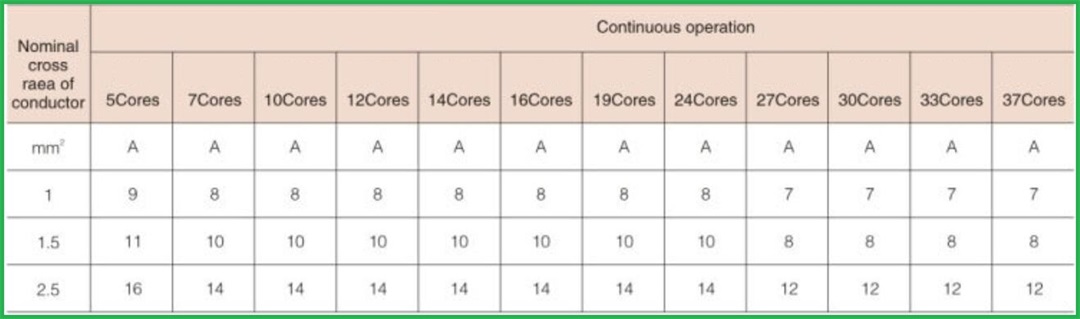
Marine cables are used to connect various electrical equipment in the ship's power grid to transmit electric energy or electrical signals. With the continuous improvement of ship electrification and automation, the variety and amount of marine cables are increasing. Marine cables are basically divided into three categories: power cables, communication cables and special high-frequency cables. Among them, power cables are used in power, lighting and other systems and are the most used cables on board. For power cables, the current carrying capacity is an important technical index. The current carrying capacity generally depends on the temperature resistance grade of the cable insulation material. Under the same laying conditions, the higher the temperature resistance level, the greater the current carrying capacity. If the ambient temperature is high and the selected cable insulation temperature resistance level is low, so that the allowable temperature rise caused by current heating is very low, it is not economical. The sheath of marine cable shall be resistant to moisture, oil, combustion and heat aging. Common sheath materials include neoprene, chlorosulfonated polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride, and lead sheath.
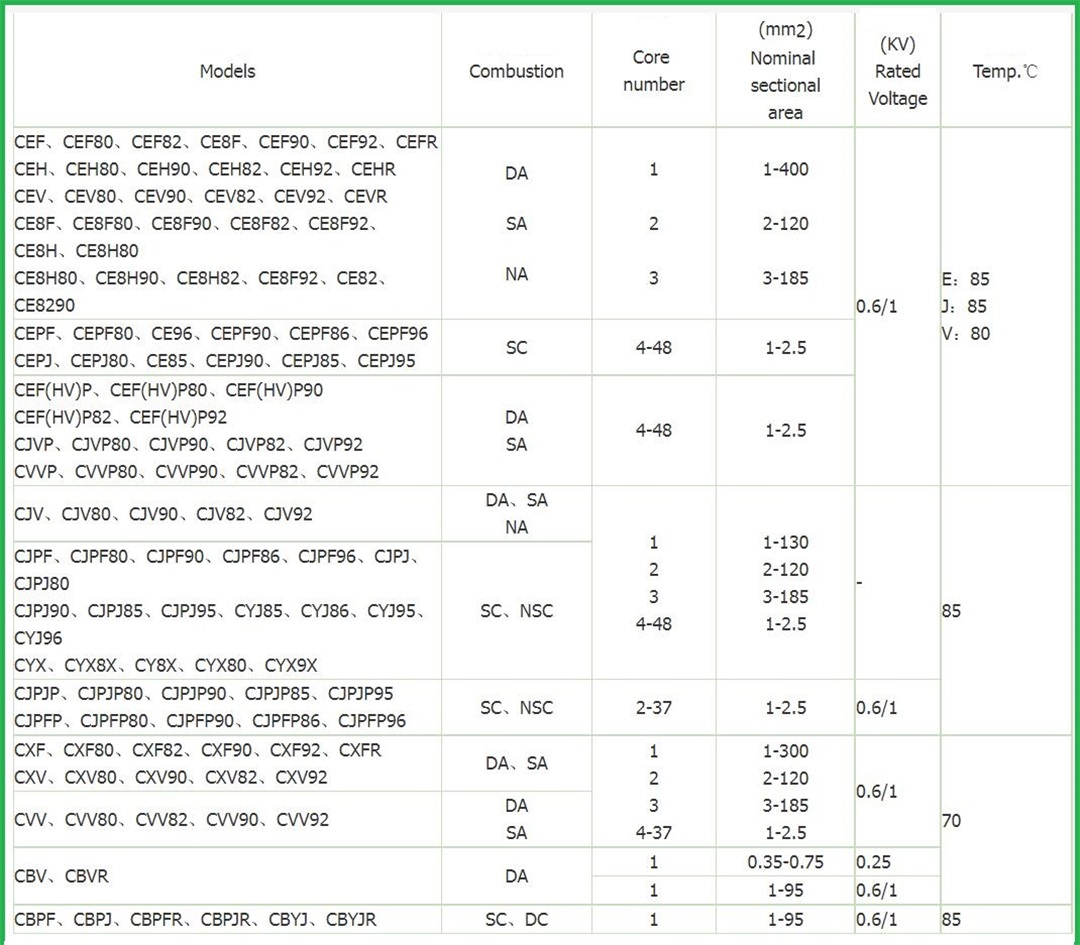
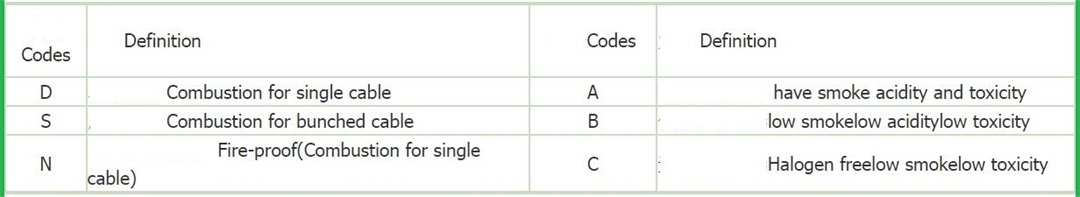
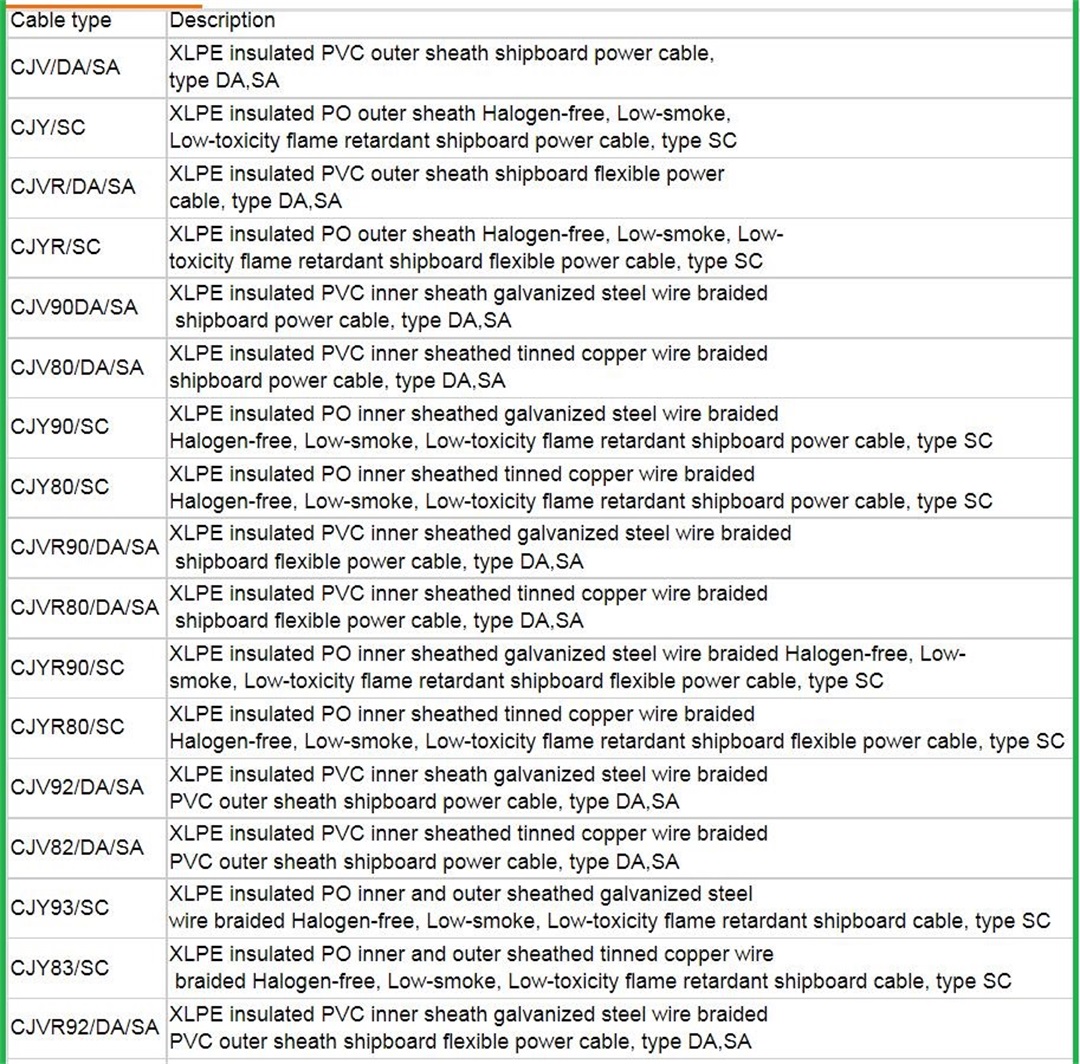
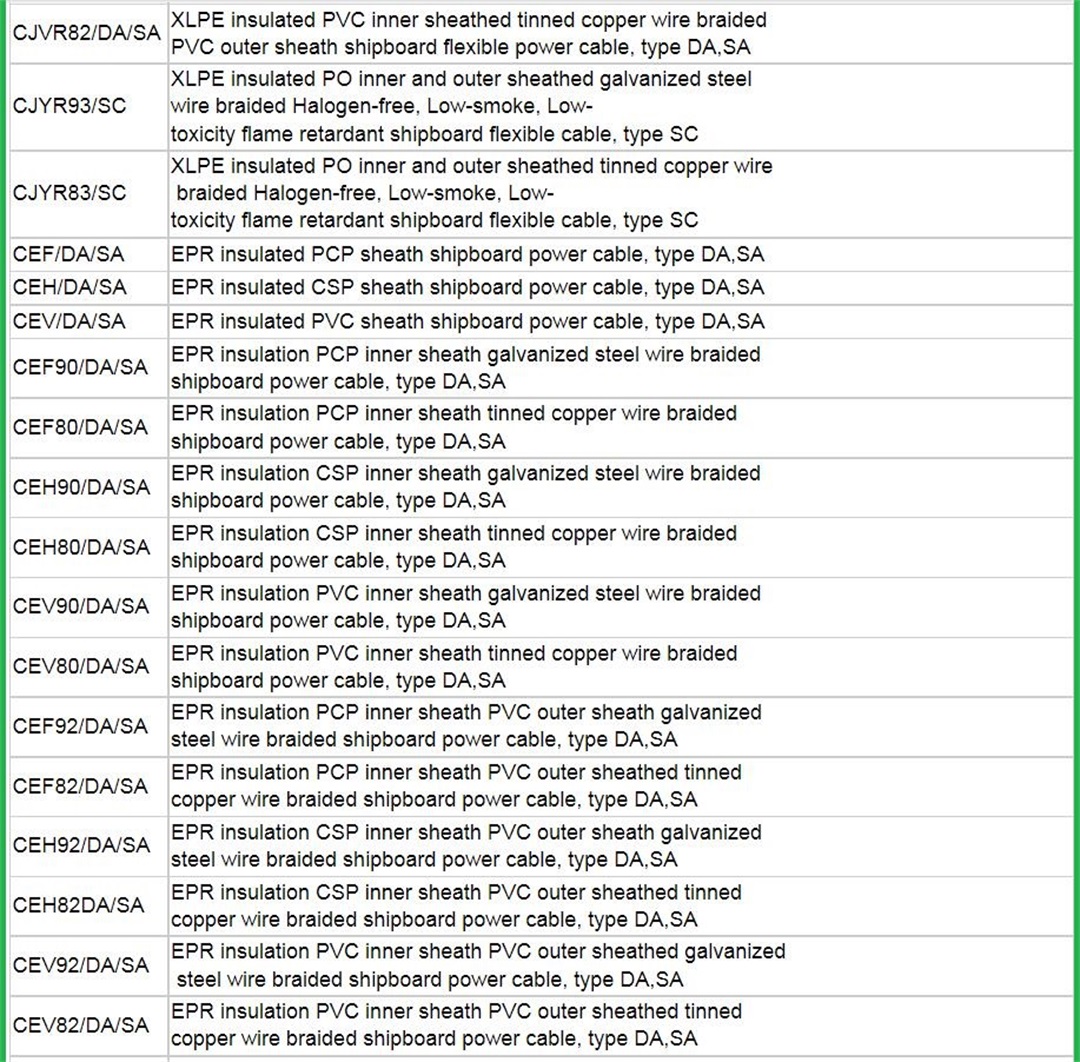
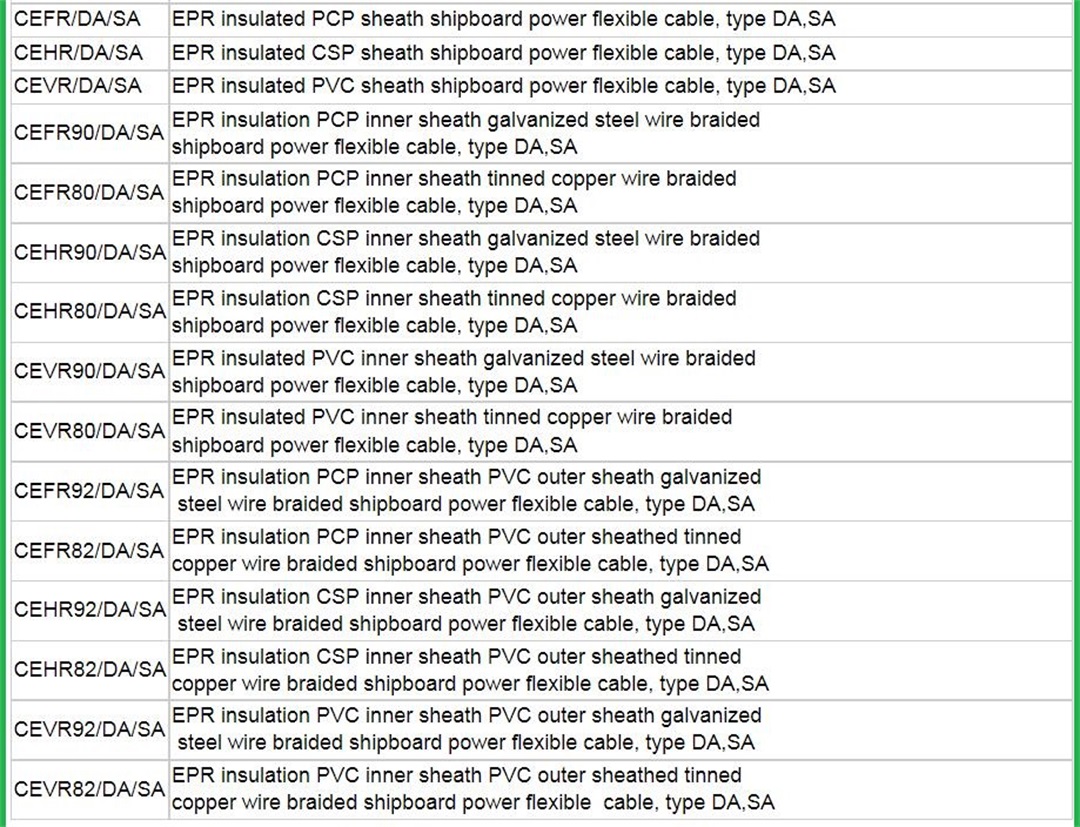
The marine power cables (DA, DB, DC, SA, SB, SC, NA, NB, NC type) with rated voltage of 0.6/1KV and below shall be produced according to GB9331-88, 92-350, 332-3. The above products are suitable for the power transmission of river and sea ships and water buildings.
This product can use ethylene-propylene insulation, cross-linked polyethylene insulation, polyvinyl chloride insulation, natural-butadiene-styrene insulation to produce marine power cables according to user needs.
The cable has the characteristics of softness, weather resistance and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for fixed installation on the hull that is not subject to mechanical stress, such as various river and sea ships and offshore oil platforms and other water structures for power transmission.
Mainly used in shipyards as well as crane equipment in the road and mining industries. The durable and wear-resistant outer sheath and the optimized lay pitch allow the cable to be used in drag chains, control platforms, water pumps and similar applications. The cable is soothing to reactions and UV radiation and is resistant to oils and petrol. Can be used in waste water and salt water.

Product features
Due to the high conductivity and high mechanical strength of copper conductors, power cables often use copper as the conductor core material. In order to improve the conductivity of conductors and prevent electrochemical corrosion, single conductor wires are often tinned to become tinned copper wires. The cable conductor can be divided into compact and non compact type according to the manufacturing process. The compact cable conductor can save materials and reduce costs, but a single conductor is no longer a regular circle. In addition to conductors with small cross section, cable conductors are usually stranded structures, which can ensure high flexibility and strong flexibility of cables, and are not prone to insulation damage and plastic deformation. From the appearance of the cable, the stranded conductor can be divided into sector, circle, hollow circle, etc. According to the number of cable conductor cores, cables can also be divided into single core cables and multi-core cables.
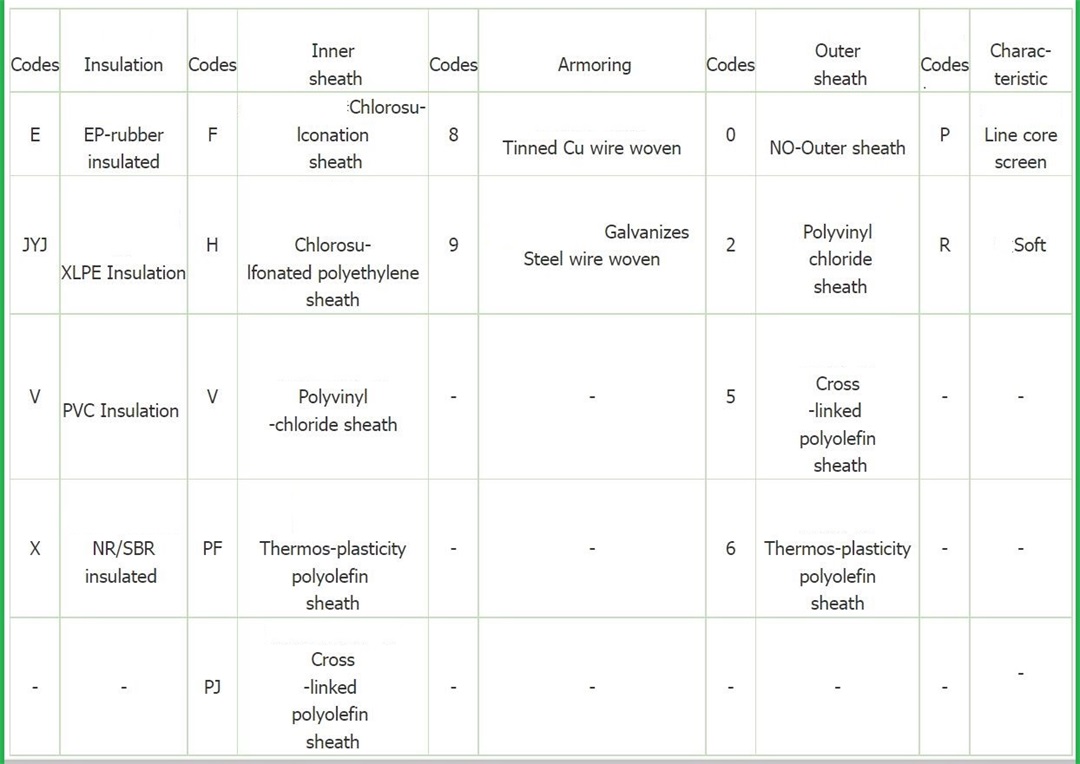
The insulation quality and level of power cables play a decisive role in the structure of the service life of cables. Marine power cables are classified according to the commonly used insulation types.
Cable filling and shielding layer
The gap between the multi-core cable cores must be filled with materials (such as non hygroscopic materials), which can not only separate the filler from the sheath, but also extrude the filler and the sheath into a whole, and can also wrap the non hygroscopic tape between the core and the sheath. In addition, there is a shielding layer inside the cable to optimize the electric field distribution inside the cable. The cable conductor is usually twisted by multiple wires. There must be a gap between the conductor and the insulation layer, and the local electric field will be concentrated. Setting an internal shielding layer between the conductor and the insulation layer can effectively solve this problem and prevent partial discharge between the core and the insulation layer. The external shielding layer is set between the insulation layer and the sheath to make the potential between the sheath and the shielding layer equal, and the contact between the insulation layer and the shielding layer is good, so as to avoid partial discharge.
Cable sheath
The protective layer of power cable is generally divided into two types: non-metallic and metal armored protective layer. The protective layer of the cable is mainly used to prevent mechanical damage to the cable, and to avoid the impact of environmental factors such as oil, salt and moisture on the cable insulation layer.

Product structure and technical requirements
Cable structure:
Conductor: Conductor conforms to VDE02956
Insulation: special TPE insulation, black and white insulation core, digital identification number
Central reinforcement: nylon reinforcement core or Kevlar bulletproof wire reinforced
Inner protection: inner sheath special TPU, PUR
reinforcement Parts: Braided reinforcement layer
Outer sheath: Outer sheath imported special TPU, PUR polyurethane
Product features: The
running speed can reach 180 m/min.
The inner and outer sheaths are braided with non-woven fabric to prevent friction, and the overall bearing braid prevents cable twisting.
Technical requirements:
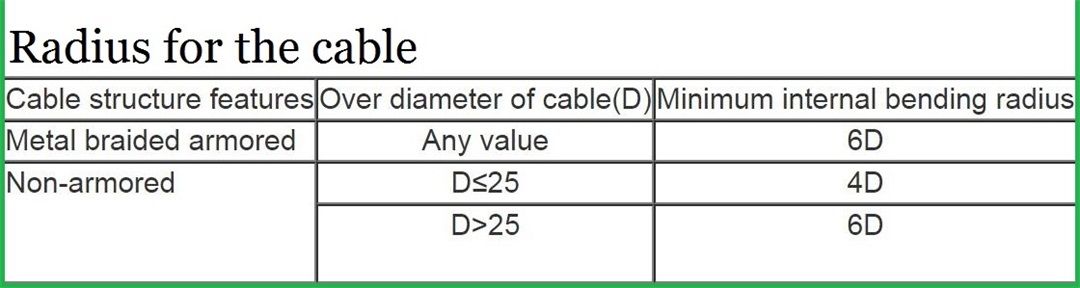
1. The allowable bending radius of the cable: the minimum is 6 times the outer diameter of the cable for unarmored cables, and 12 times the outer diameter of the cable for armored cables;
2. The product has excellent electrical and physical properties and is light in weight , Good flexibility, low smoke, halogen-free, flame retardant, low toxicity and other characteristics;
3, Rated voltage is 0.6/1KV.

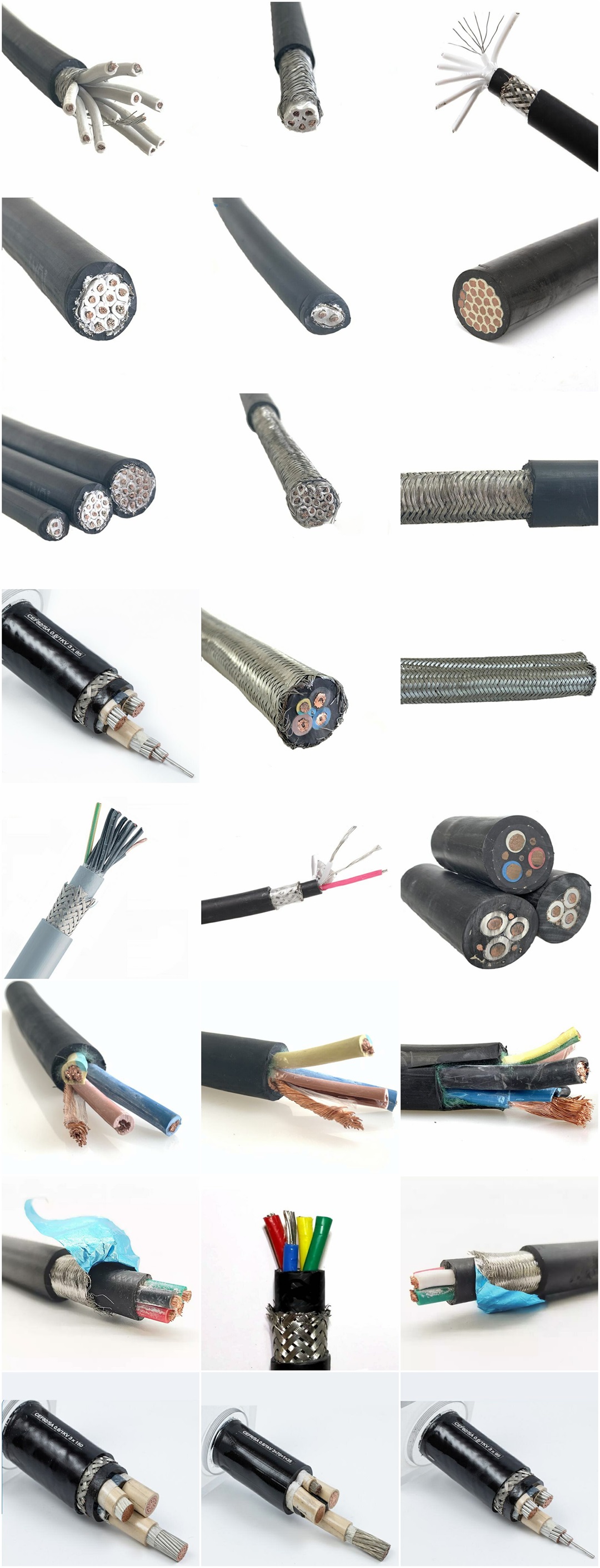
Product details

Products real shot

A corner of the production workshop

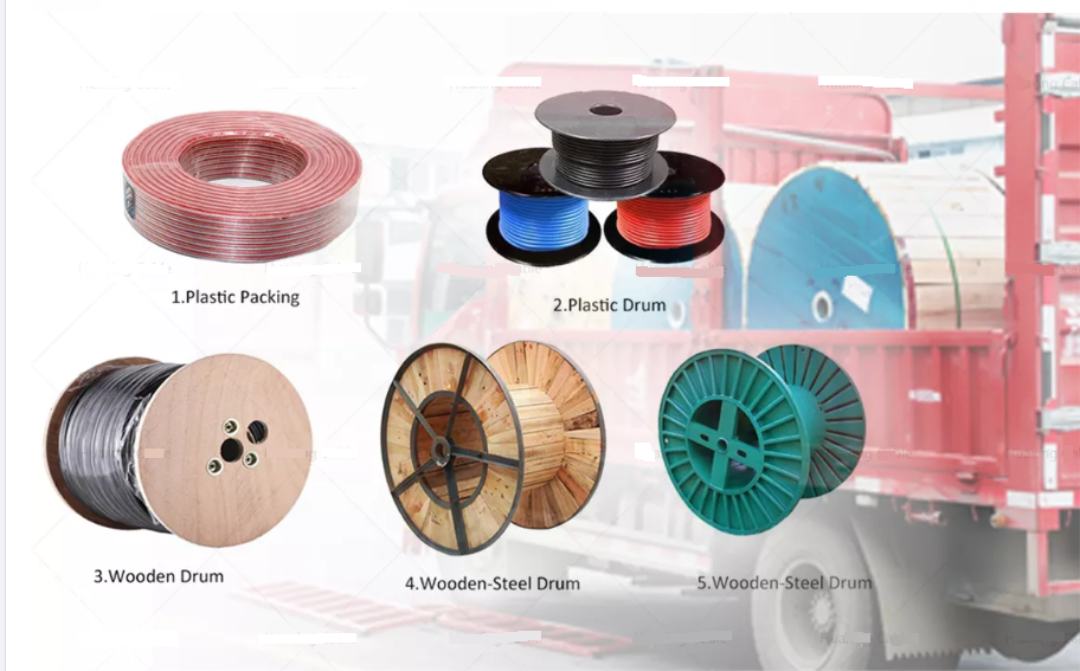
Product packaging

Product application scenarios