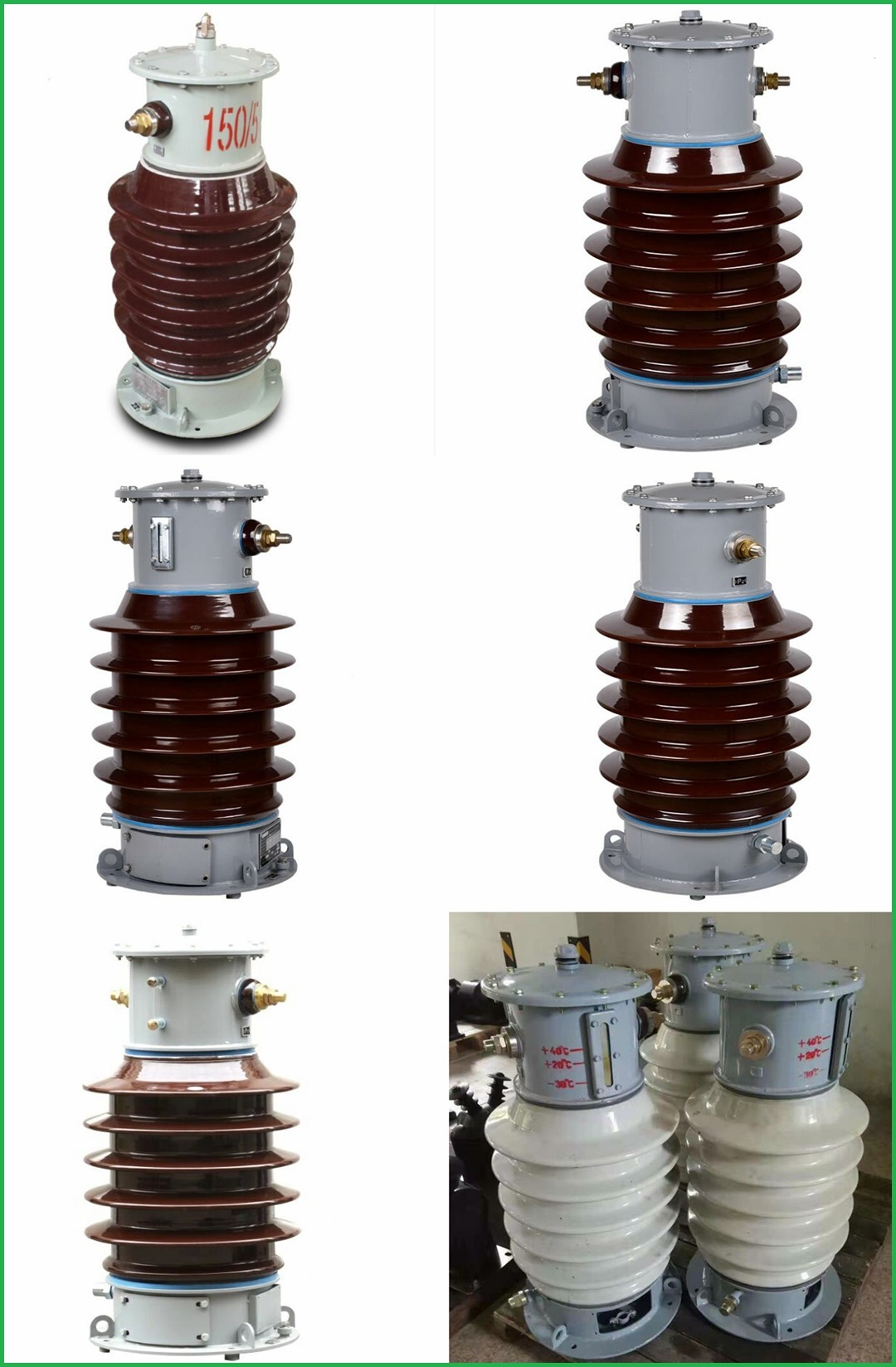
LCWD 35KV 15-1500/5 0.5/10P20 20-50VA Outdoor High Voltage Porcelain Insulated Oil-immersed Current Transformer
Product Description
LCWD-35 current transformer is oil-paper insulated, outdoor type product, suitable for electric energy measurement, current measurement and relay protection in power system with rated frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz and rated voltage of 35kV and below.

Model Description

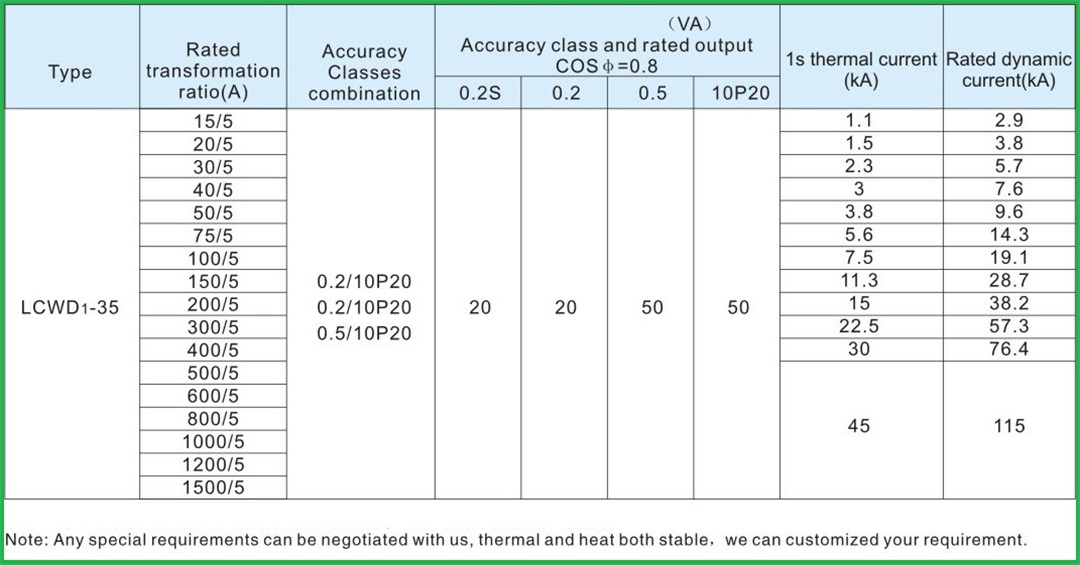
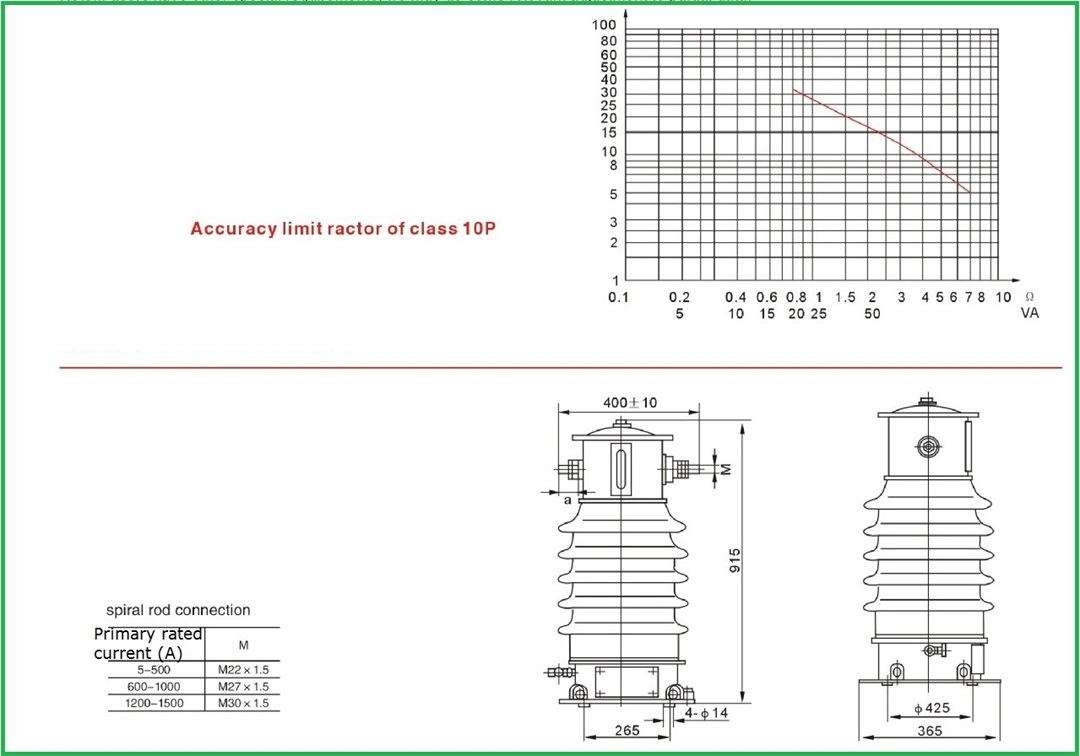
Technical parameters and structure dimensions
Product features and Principle
The LCWD-35 current transformer is compact, small in size and light in weight. The upper half is the primary winding, the lower half is the secondary winding, the bushing is fixed on the base, the top of the bushing is equipped with an oil conservator, the primary winding is led out from both sides of the cabinet wall, and the starting terminal marked P1 A small porcelain sleeve is used to insulate the cabinet wall, and the end P2 is directly connected to the cabinet wall. The front of the oil conservator is equipped with oil gauges indicating different temperatures.
Principle:
In the lines of power generation, substation, transmission, distribution and consumption, the current varies greatly, ranging from a few amperes to tens of thousands of amperes. In order to facilitate measurement, protection and control, it needs to be converted into a relatively uniform current. In addition, the voltage on the line is generally relatively high, such as direct measurement, which is very dangerous. The current transformer plays the role of current transformation and electrical isolation.
For pointer-type ammeters, most of the secondary currents of the current transformers are in the ampere level (such as 5A, etc.). For digital instruments, the sampled signal is generally at the milliamp level (0-5V, 4-20mA , etc.). The secondary current of the miniature current transformer is milliampere, which mainly acts as a bridge between the large transformer and the sampling.
Miniature current transformers are also called "instrument current transformers". ("Instrument current transformer" has a meaning that it is a multi-current ratio precision current transformer used in the laboratory, which is generally used to expand the instrument range.)
Similar to the transformer, the current transformer also works according to the principle of electromagnetic induction. The transformer transforms the voltage and the current transformer transforms the current. The winding of the current transformer connected to the measured current (the number of turns is N1) is called the primary winding (or the primary winding, the primary winding); the winding connected to the measuring instrument (the number of turns is N2) is called the secondary winding (or secondary winding). winding, secondary winding).
The current ratio of the primary winding current I1 to the secondary winding I2 of the current transformer is called the actual current ratio K. The current ratio of the current transformer when it works under the rated current is called the rated current ratio of the current transformer , expressed by Kn.
Kn=I1n/I2n
The function of the current transformer (CT for short) is to convert the primary current with a larger value into a secondary current with a smaller value through a certain transformation ratio, which is used for protection, measurement and other purposes. For example, a current transformer with a ratio of 400/5 can convert an actual current of 400A into a current of 5A.

Transformer Problem Handling and order plan
Handling of Transformer-related Problems:
Current transformer failures are often accompanied by sounds and other phenomena. When the secondary circuit is suddenly opened, a high induced potential is generated in the secondary coil, and its peak value can reach more than several thousand volts, which endangers the life of the staff and the safety of equipment on the secondary circuit, and the high voltage may cause arc fire. At the same time, due to the sharp increase of the magnetic flux in the iron core, it reaches a high saturation state. The core loss and heat are serious, which may damage the rheological secondary winding. At this time, the non-sinusoidal wave is caused by the increase of the magnetic flux density, which makes the vibration of the silicon steel sheet extremely uneven, resulting in a large noise.
1. Handling of the current transformer in the open circuit If such a fault occurs, the load should be kept unchanged, the protection device that may be malfunctioning should be deactivated, and the relevant personnel should be notified to eliminate it quickly.
2. Treatment of current transformer secondary circuit disconnection (open circuit) 1. Abnormal phenomenon:
a. The indication of the ammeter drops to zero, the indication of the active and reactive power meters decreases or oscillates, and the watt-hour meter rotates slowly or stops.
b. Differential disconnection light plate warning.
c. The current transformer makes abnormal noises or generates heat, smokes or discharges from the secondary terminals, sparks, etc.
d. The relay protection device refuses to act, or malfunctions (this phenomenon is only found when the circuit breaker trips by mistake or refuses to trip and causes a leapfrog trip).
2. Exception handling:
a. Immediately report the symptom to the schedule to which it belongs.
b. According to the phenomenon, judge whether the current transformer of the measurement circuit or the protection circuit is open. Deactivation of protections that may cause erroneous operation should be considered before disposal.
c. When checking the secondary circuit of the current transformer, you must stand on the insulating pad, pay attention to personal safety, and use qualified insulating tools.
d. When the secondary circuit of the current transformer is open to cause a fire, the power should be cut off first, and then the fire should be extinguished with dry asbestos cloth or dry fire extinguisher.
3. Current transformer body fault When the current transformer fault has one of the following conditions, it should be stopped immediately:
a. There is abnormal sound and overheating inside, accompanied by smoke and burnt smell. b. Serious oil leakage, damaged porcelain or discharge phenomenon.
c. Fuel injection fire or glue flow phenomenon.
d. The elongation of the metal expander significantly exceeds the specified value at ambient temperature.
Order plan:
1. Provide wiring scheme diagram, application and system diagram, rated voltage, rated current, etc.
2. Requirements for control, measurement and protection functions and other locking and automatic devices.
3. When the transformer is used in special environmental conditions, it should be explained in detail when ordering.
4. When other or more accessories and spare parts are needed, the type and quantity should be proposed.

Products real shot

A corner of the production workshop
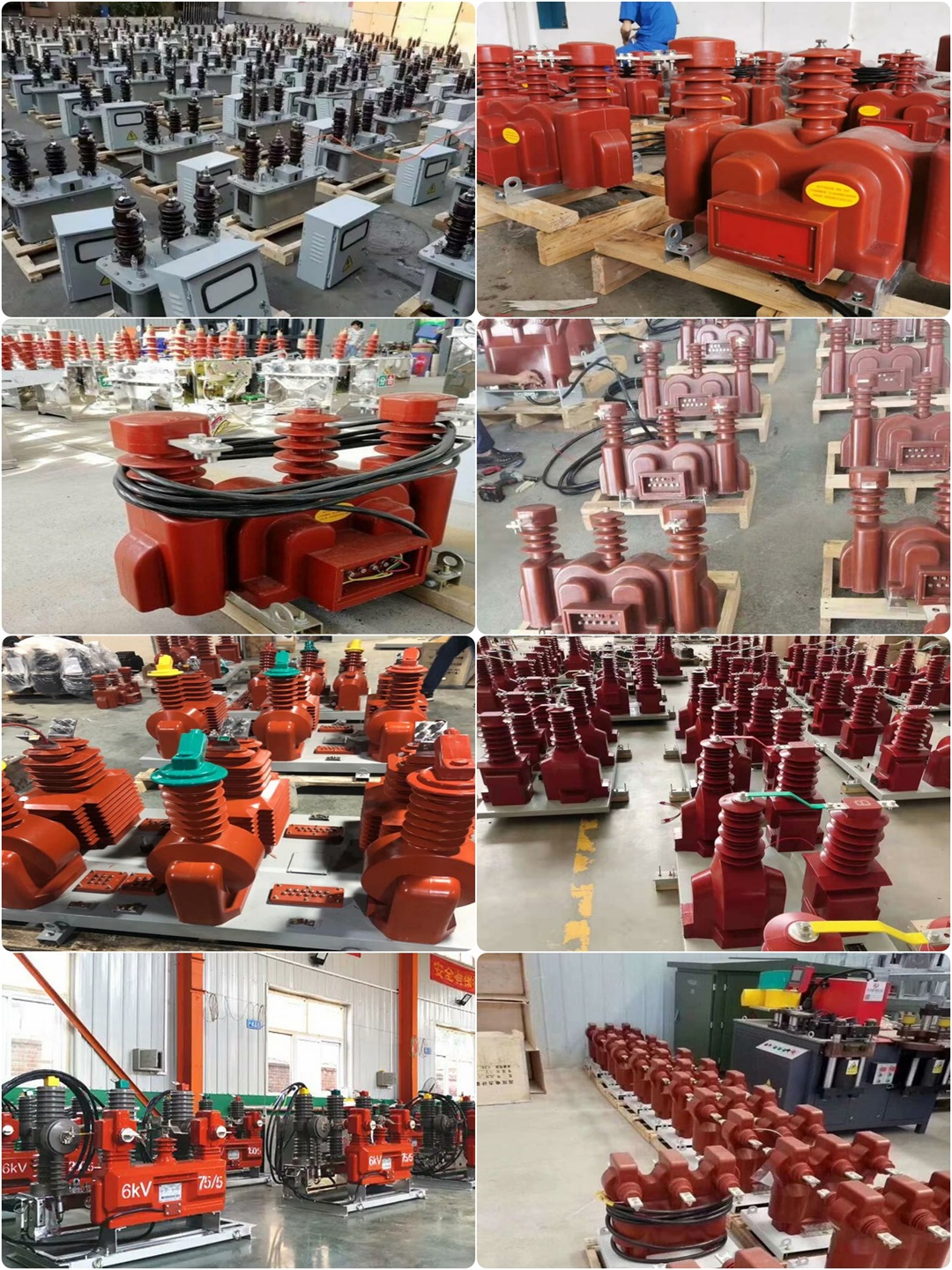


Product packaging

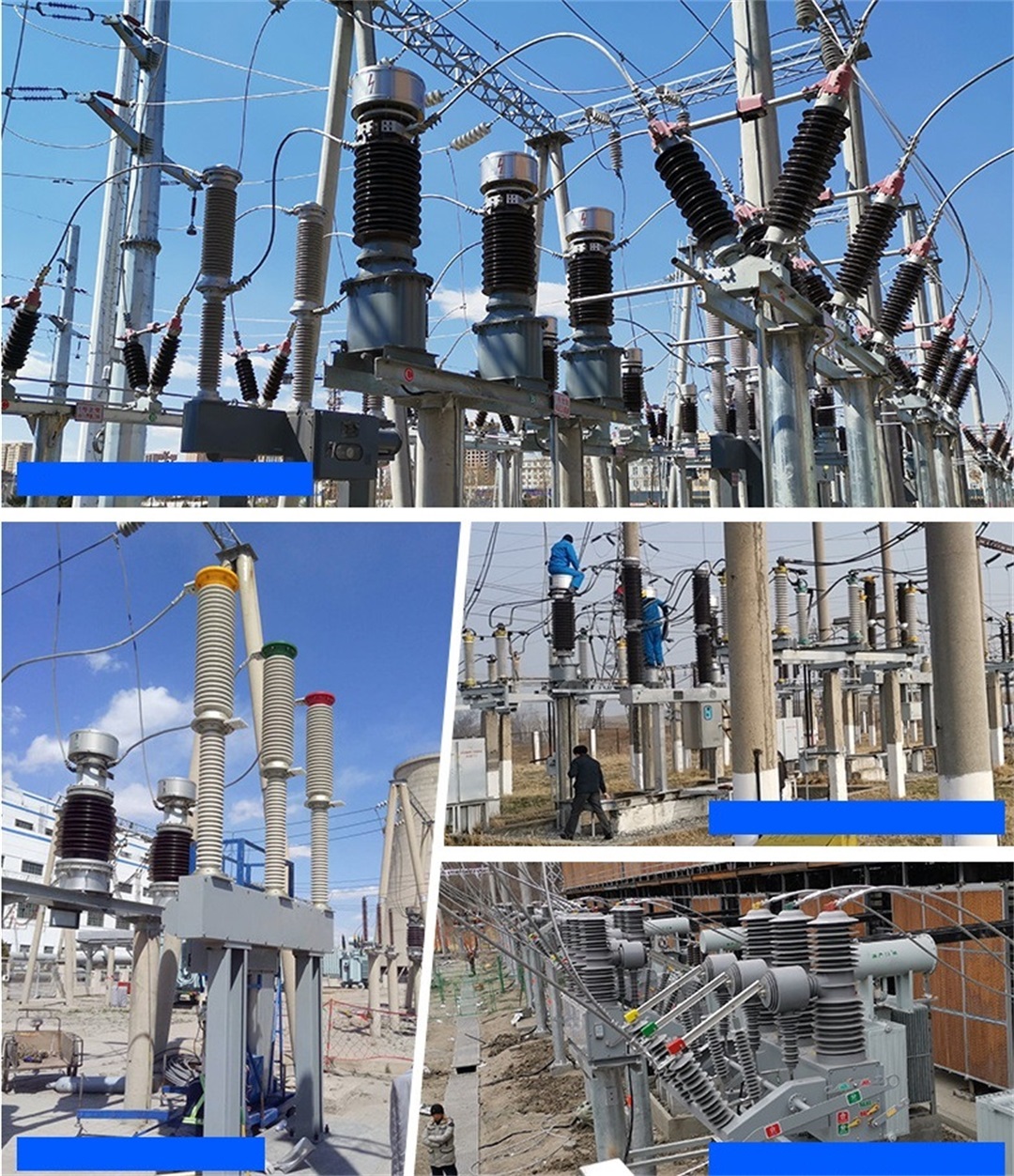
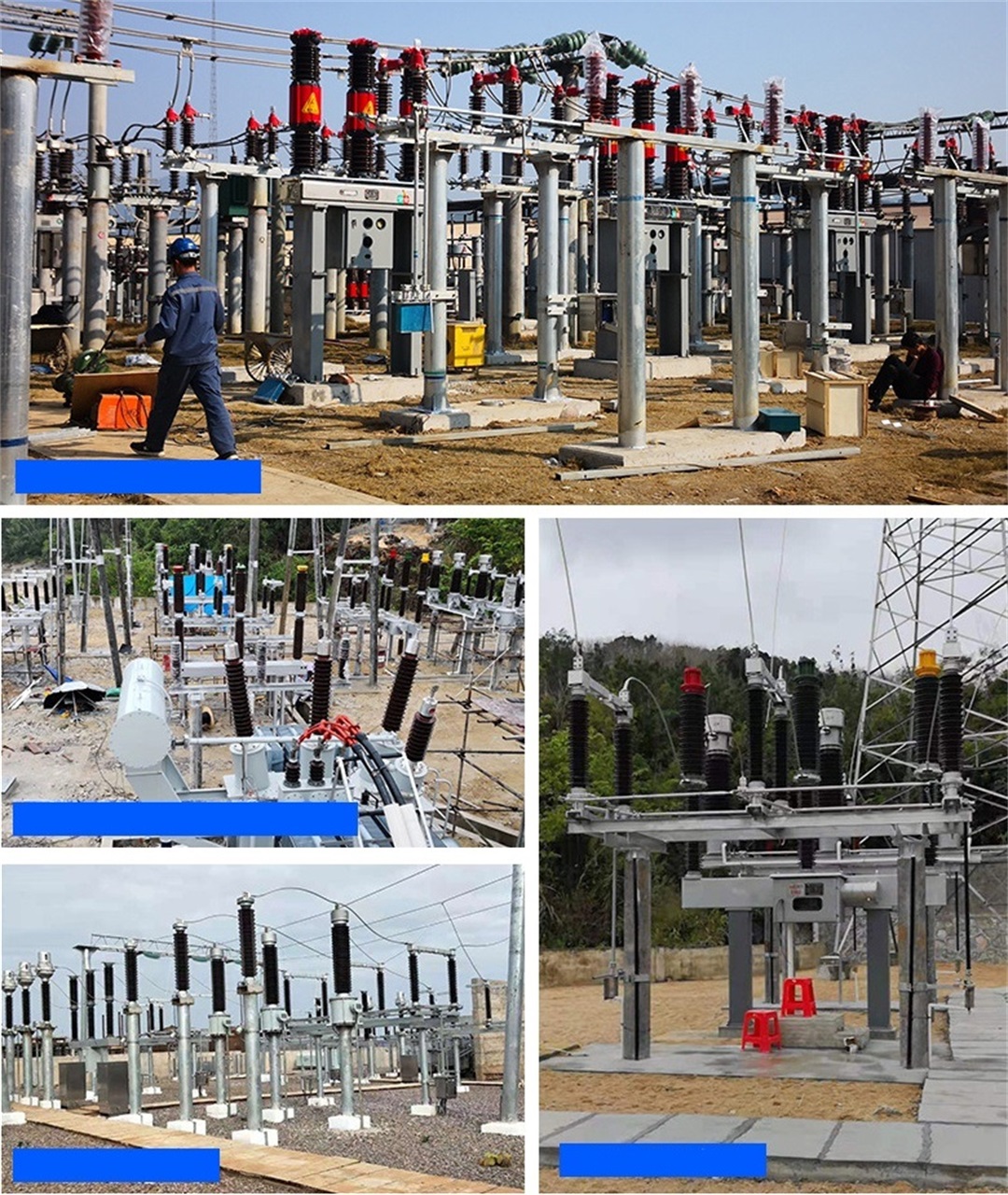
Product application case